Nodes
Nodes
Understanding DAIANA STUDIO Nodes
In this article, we use 🧷LangChain nodes when creating chat flows. You will find detailed explanations about these fundamental nodes on the dedicated 🧷LangChain page, so we recommend you consult it for more information.
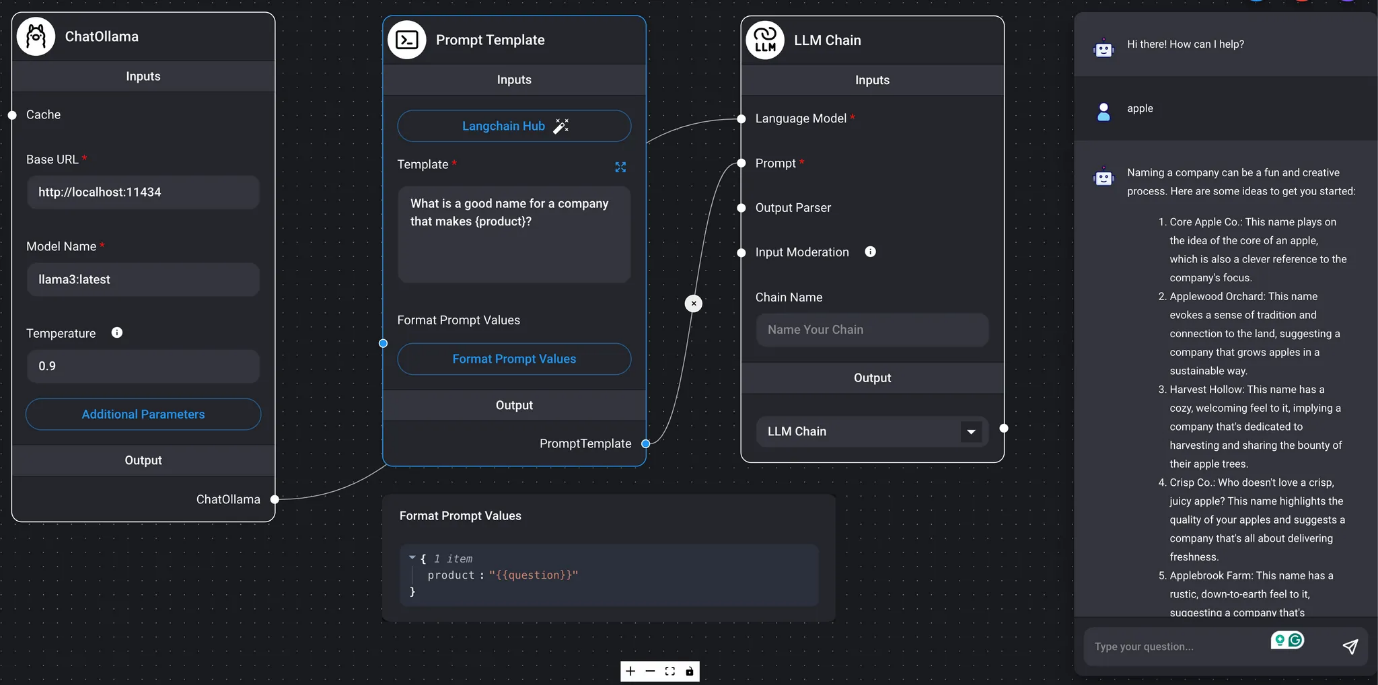
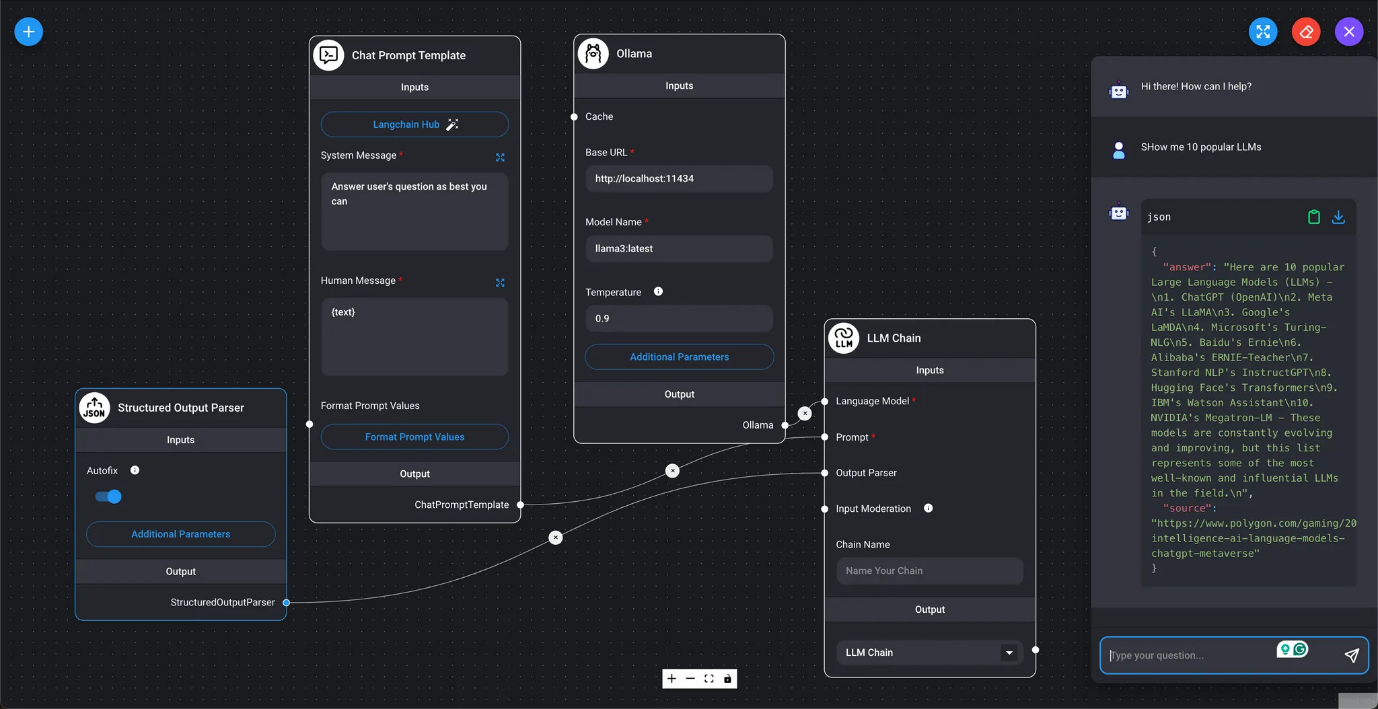
DAIANA STUDIO nodes are divided into inputs and outputs. They calculate outputs from inputs, sequentially passing data to the next node as input. In the final node (chain), the result of the LLM query is obtained and displayed in the chat box.
In the diagram below, the output of the ChatOllama / Prompt Template nodes becomes the input for the final LLM Chain node. From these values, the result of the LLM query is displayed as the LLM's response in the chat dialog box.
Introduction 🦜️🔗 LangChain
Chain
When querying the LLM, by inserting the Prompt and Output Parser processes before and after the language model, a single chain node is created, and the connection between the chain nodes is enabled.
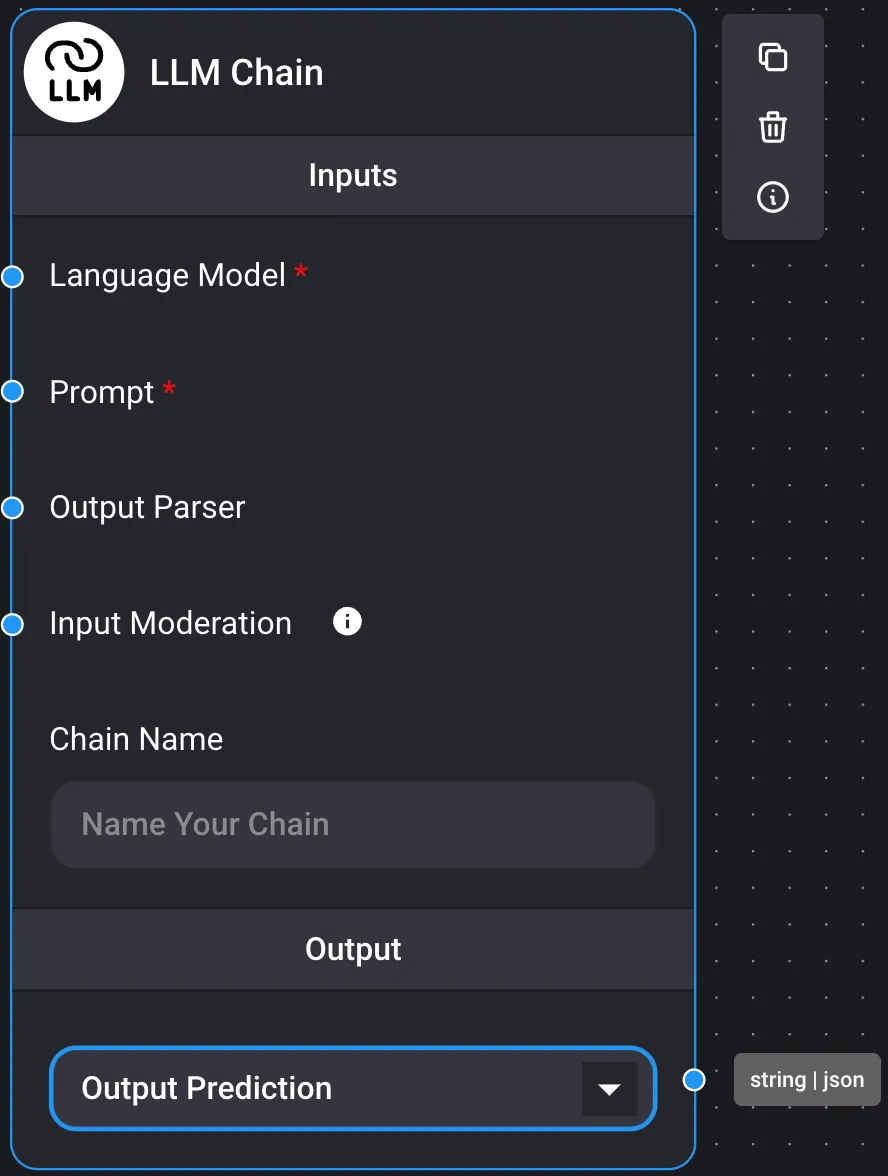
Chains are classified into the following four groups. If the output of a chain node is executable, the result of the LLM query will be obtained in the chat box as the final node.
- An example where the output serves as input for other nodes, as the output is not executable
- Output Chain | json
- An example where it acts as the final node of the chain, generating the result of the LLM query, as the output is executable.
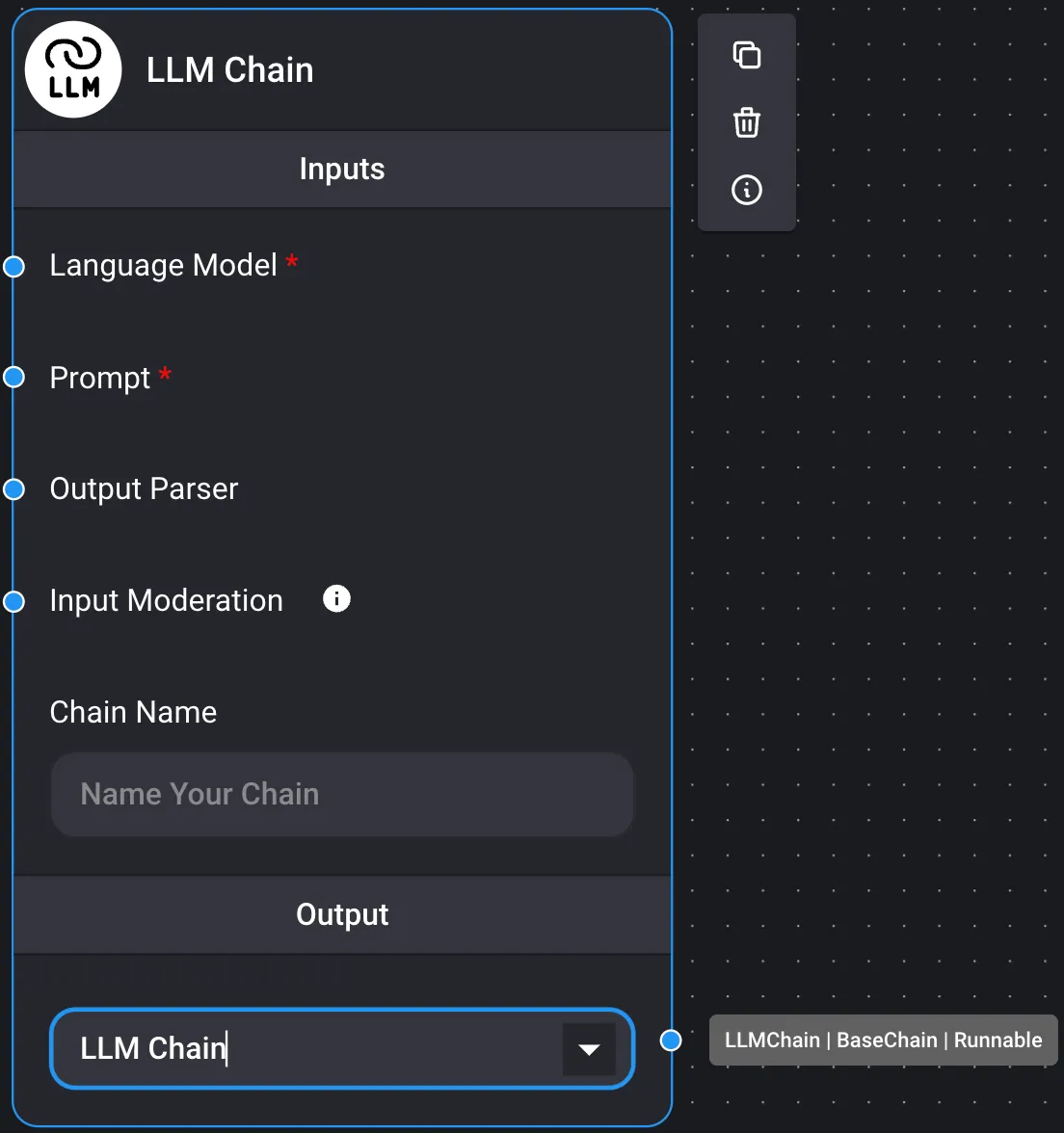
- Executable output

It is recommended to consult the Marketplace for usage examples.
- Prompt Chains
- LLM Chain
- Marketplace / Simple LLM Chain
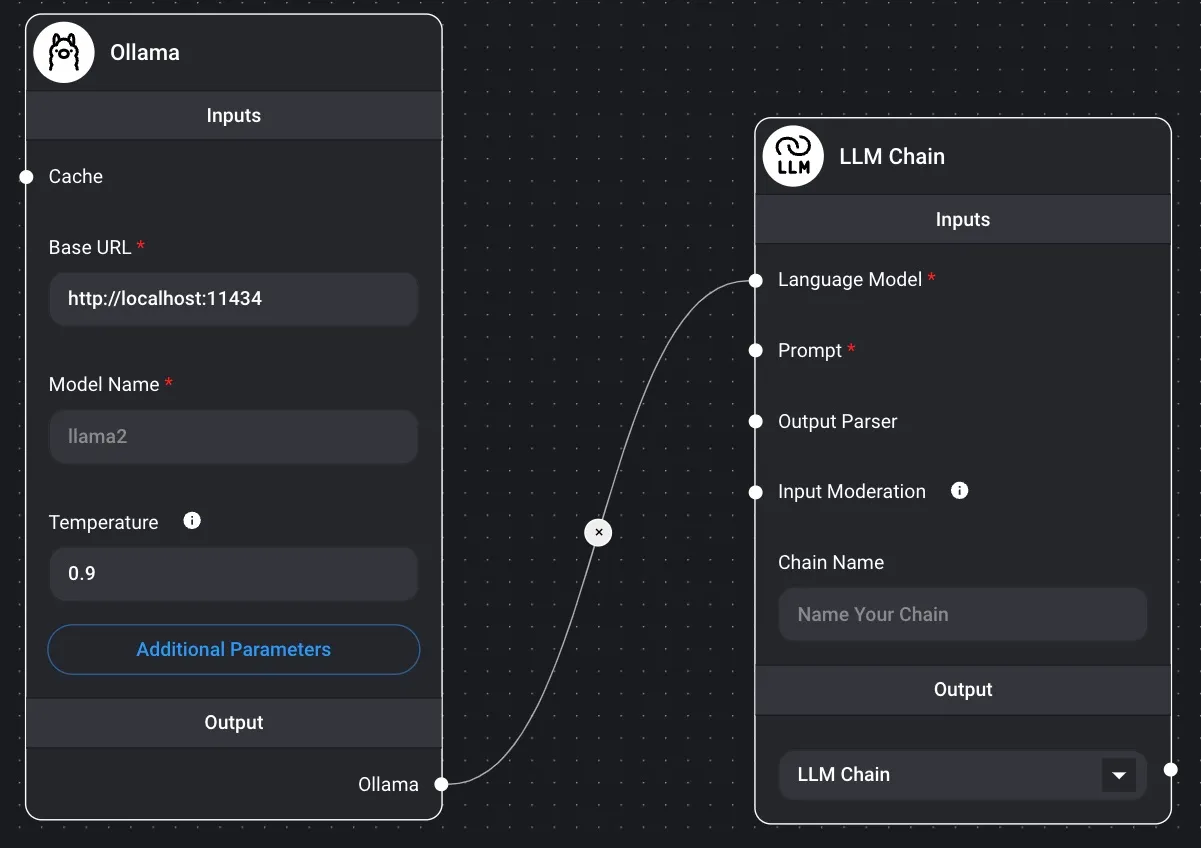
Below is a basic example of a stateless LLM chain (without memory) that uses a prompt template and an LLM model.
It is possible to set an input value from the chat dialog as a prompt value.
- Marketplace / Fast Chaining
It is possible to use the result of one chain as a prompt for another chain.
By configuring the output of an LLM chain as an output prediction, the result can be passed as a variable to the prompt template. To get the final answer from the LLM chain result, the output is configured in the LLM chain.
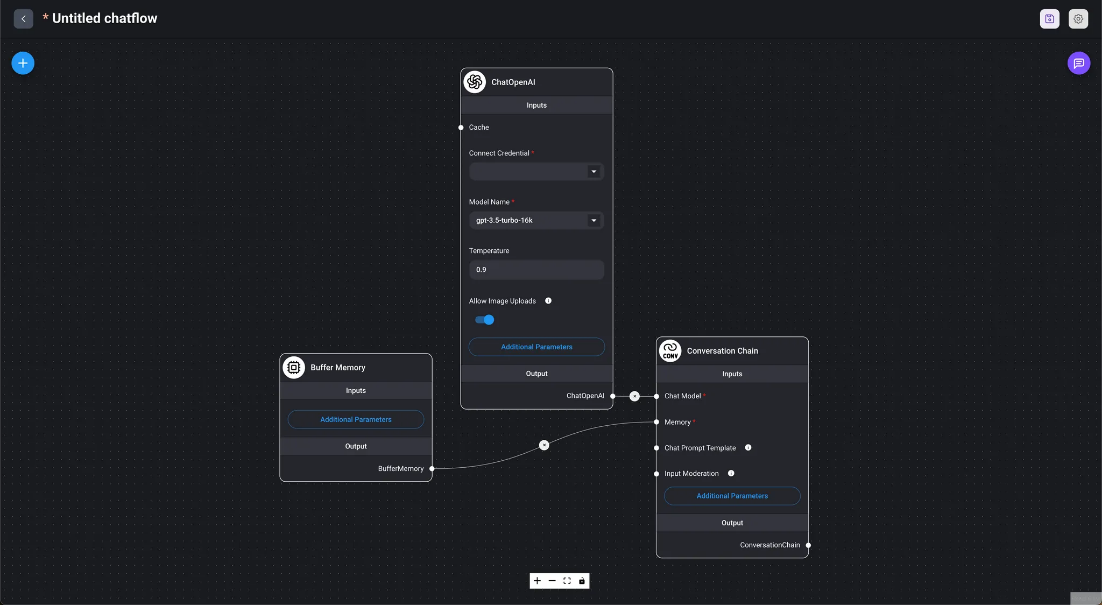
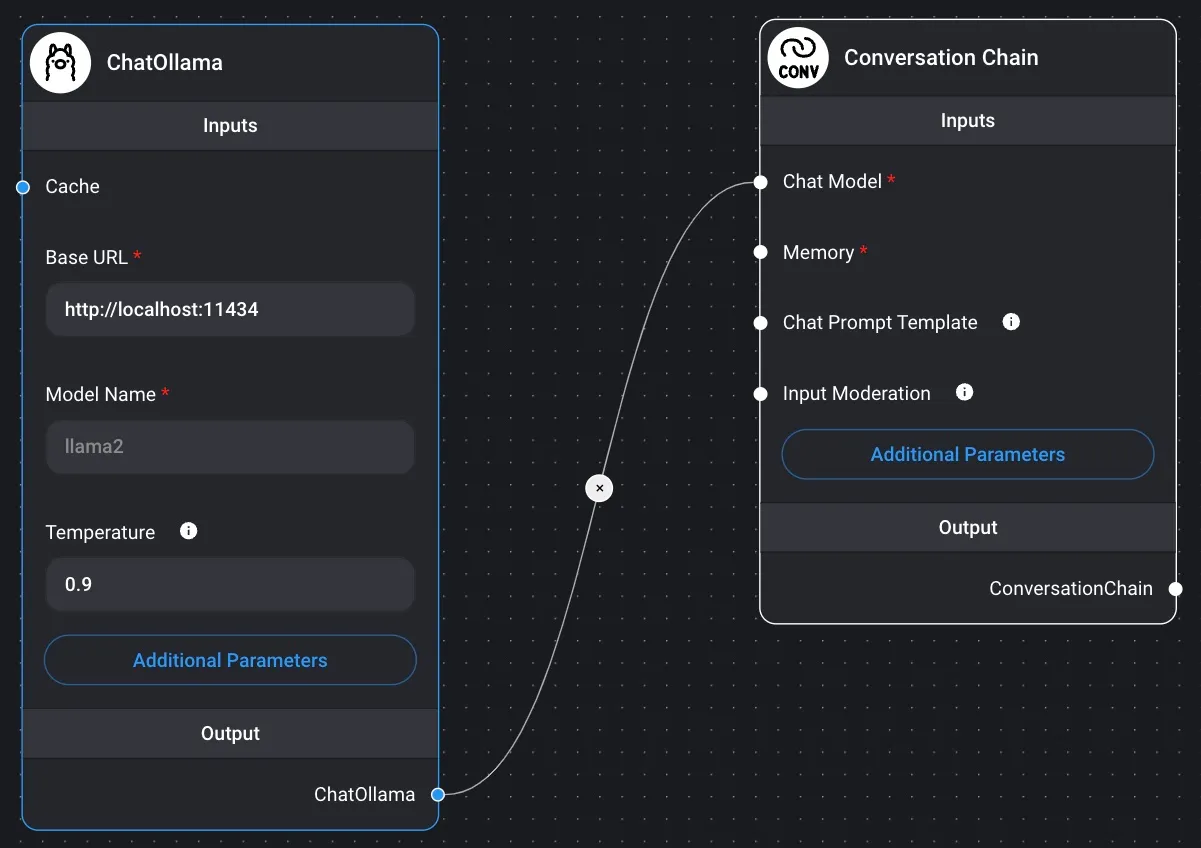
- Conversational Chain
- Marketplace / Simple Conversational Chain This is a basic example of a conversational chain that uses built-in memory and functions similarly to ChatGPT.
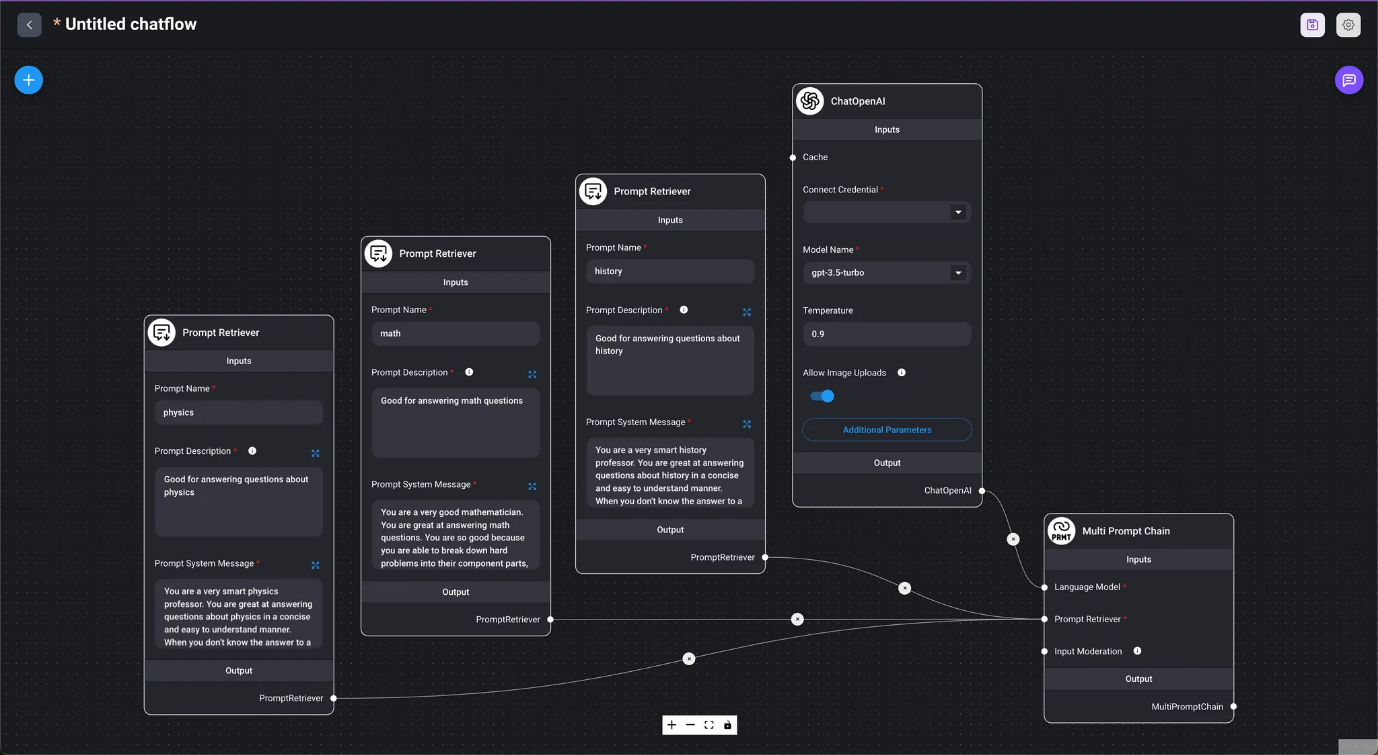
- Multi-prompt Chain
- Marketplace / Multi-prompt Chain Automatically selects an appropriate prompt based on the value entered in the chat dialog box and provides a response.
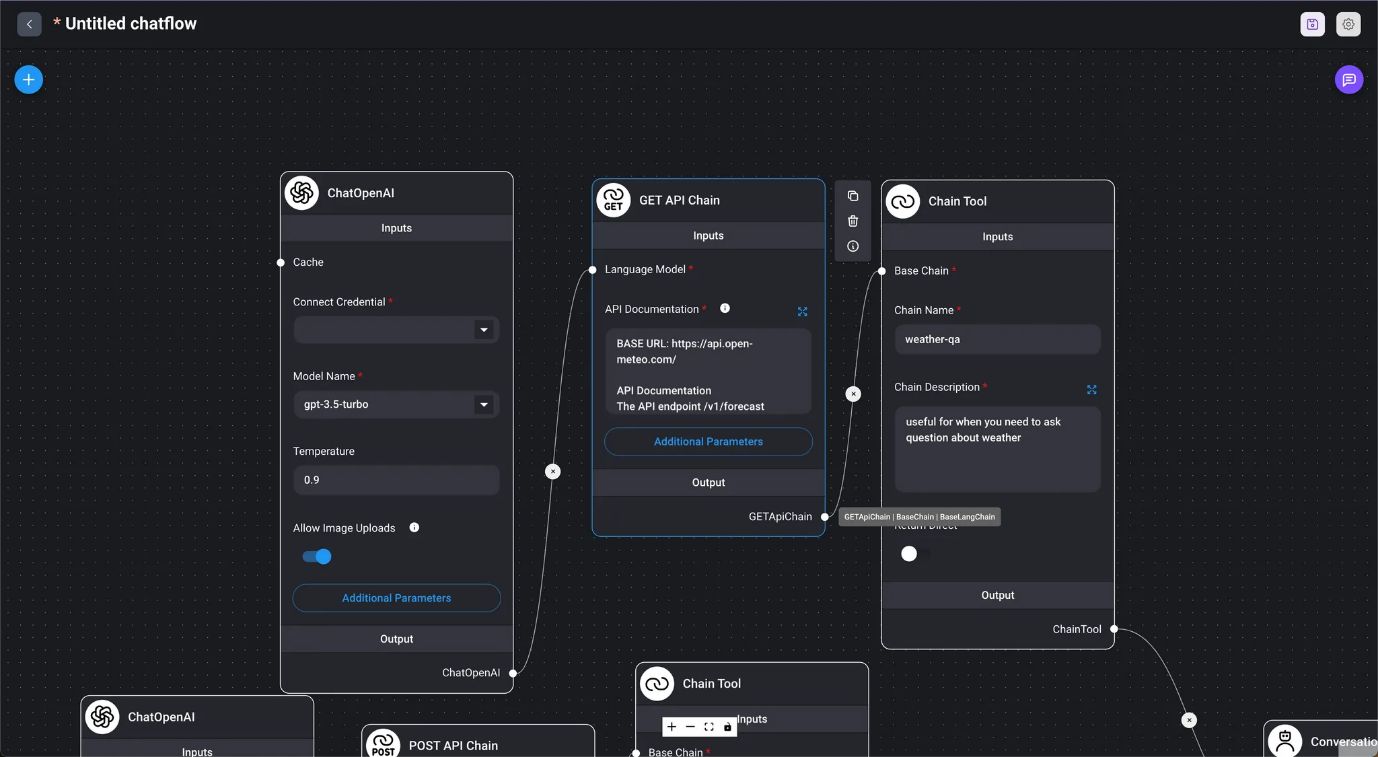
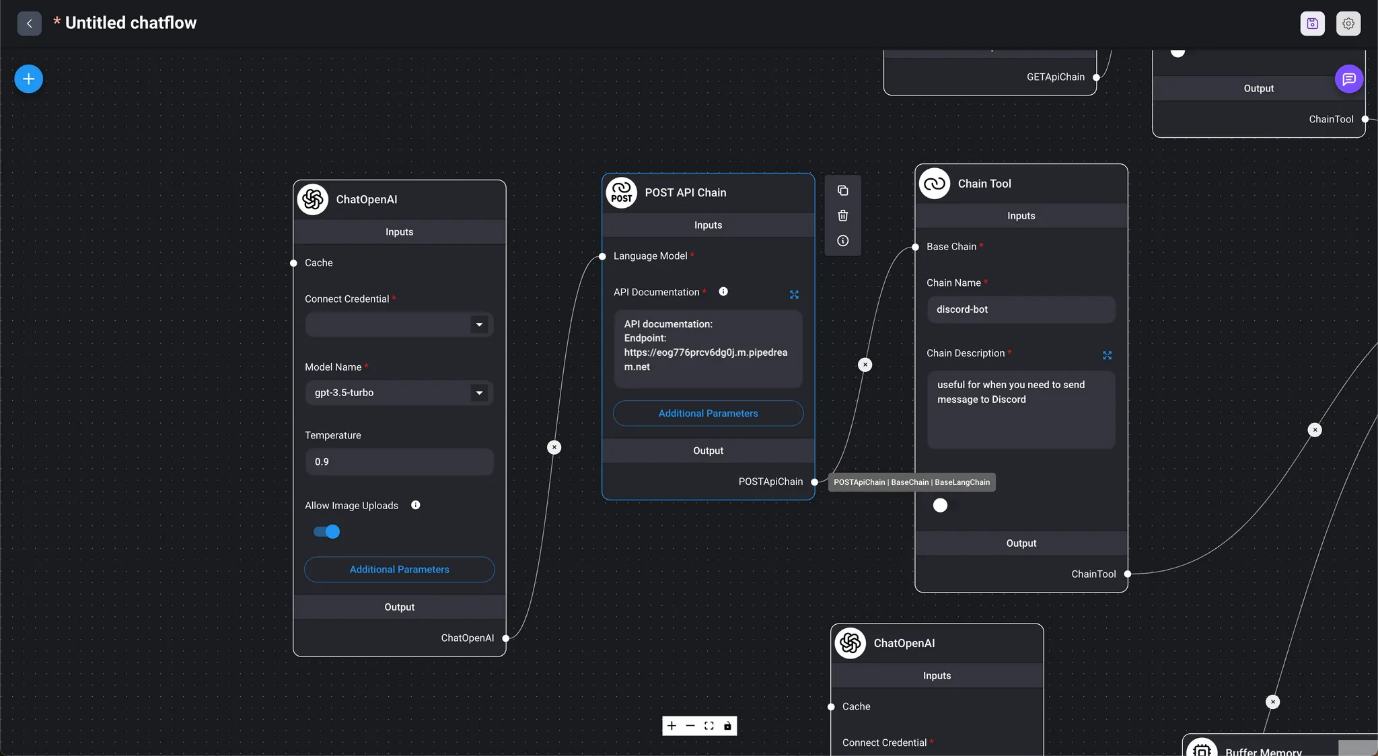
- API Chains
- API POST Chain
- Marketplace / API Agent When provided with API documentation, the agent automatically determines which API to call and generates the URL and request body from the conversation.
- API GET Chain
- Marketplace / API Agent When provided with API documentation, the agent automatically determines which API to call and generates the URL and request body from the conversation.
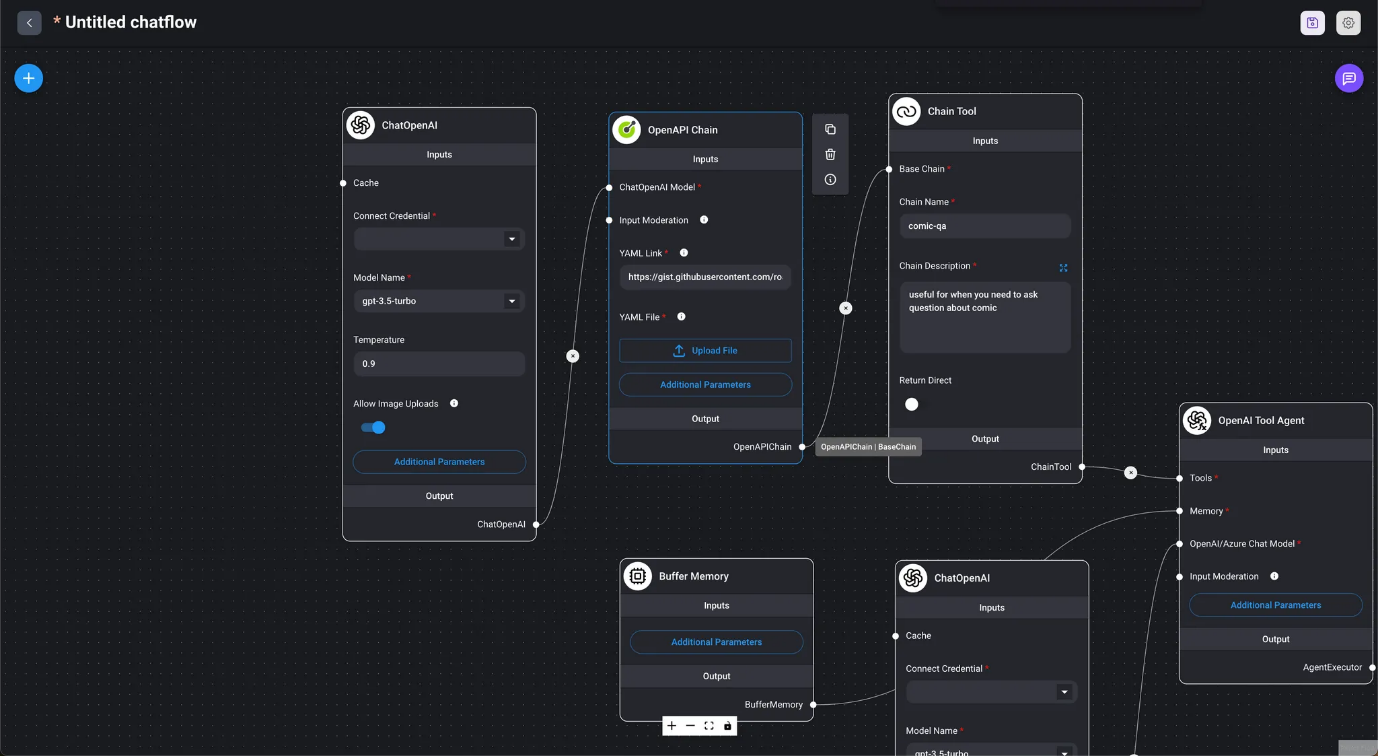
- OpenAPI Chain
- Marketplace / OpenAI API Agent Using the OpenAPI Tool Agent and Chain, it automatically determines which API to call and generates the URL and request body from the conversation.

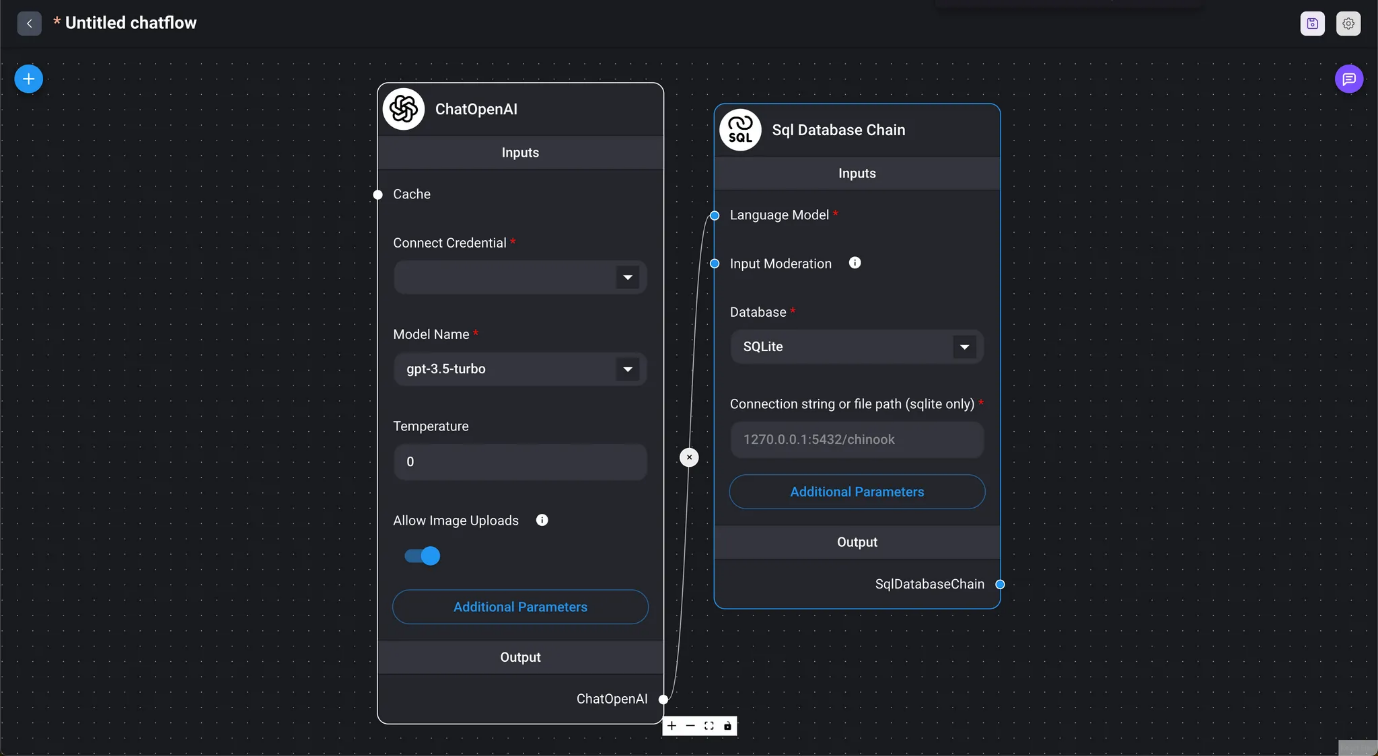
Use an SQL database to answer.
- Vectara QA Chain
- Marketplace / Vectara RAG Chain
- QA Chain for Vectara
- VectorDB QA Chain
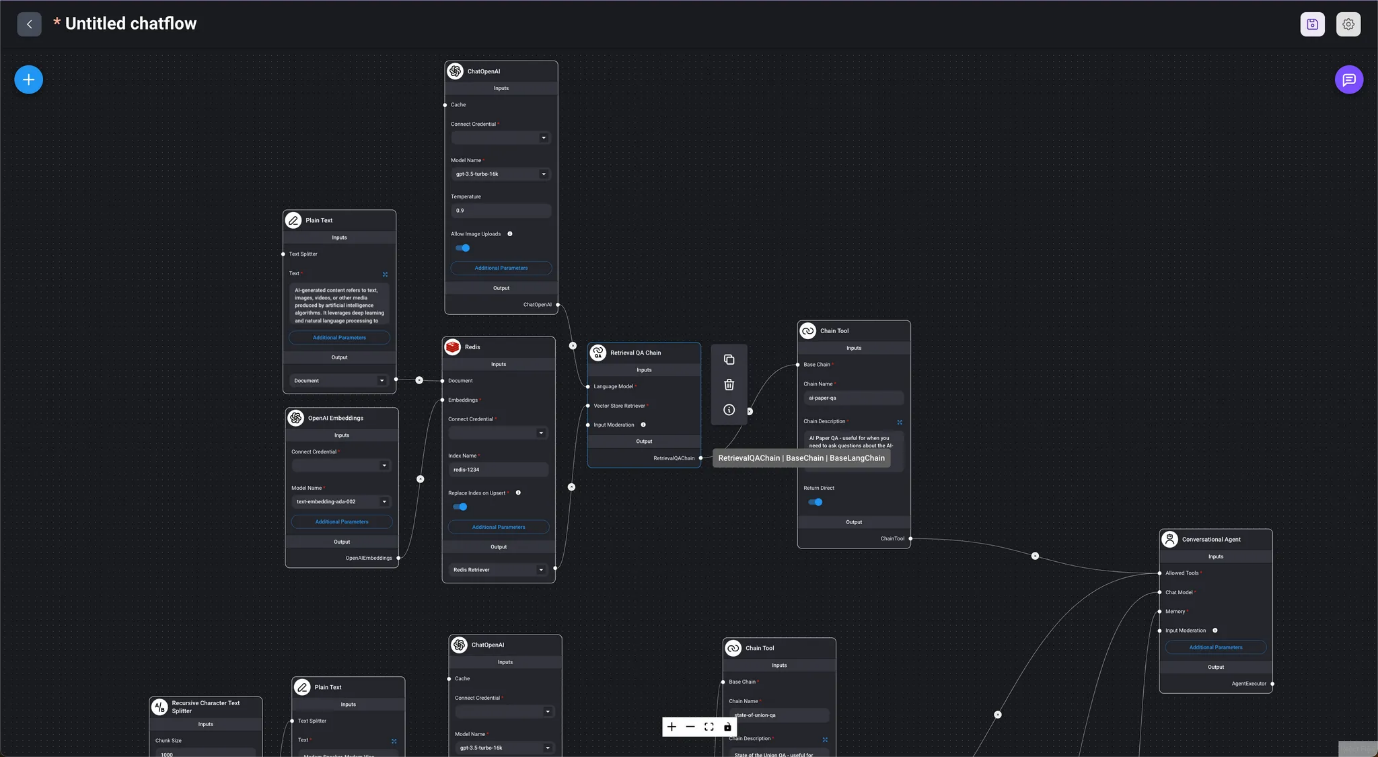
- Retrieval Chains
- Retrieval QA Chain
- Marketplace / Multi VectorDB Using the agent to select VectorDB.
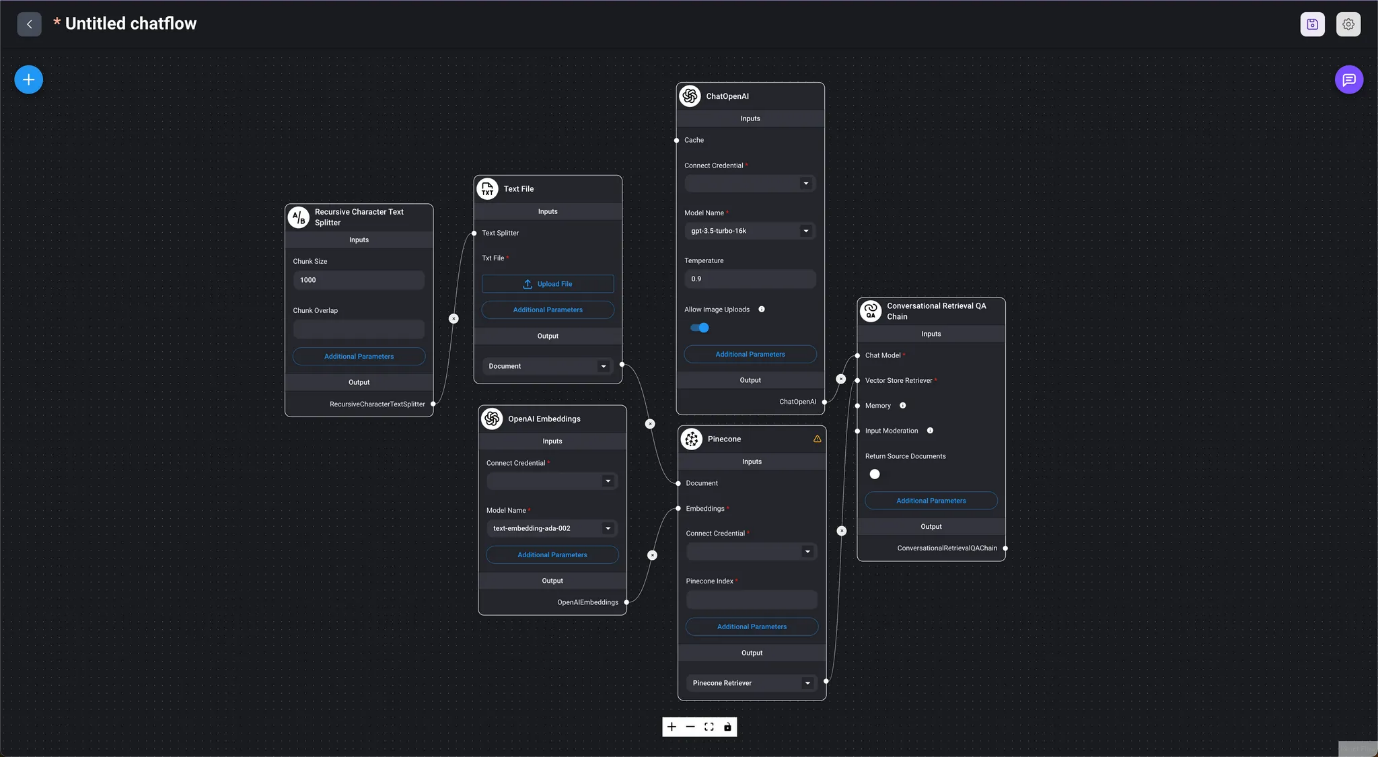
- Conversational Retrieval QA Chain
- Marketplace / Conversational Retrieval QA Chain Using the conversational retrieval QA chain for a Q&A session with a text file.
- Multi-Retrieval QA Chain
- Marketplace / Multi-Retrieval QA Chain
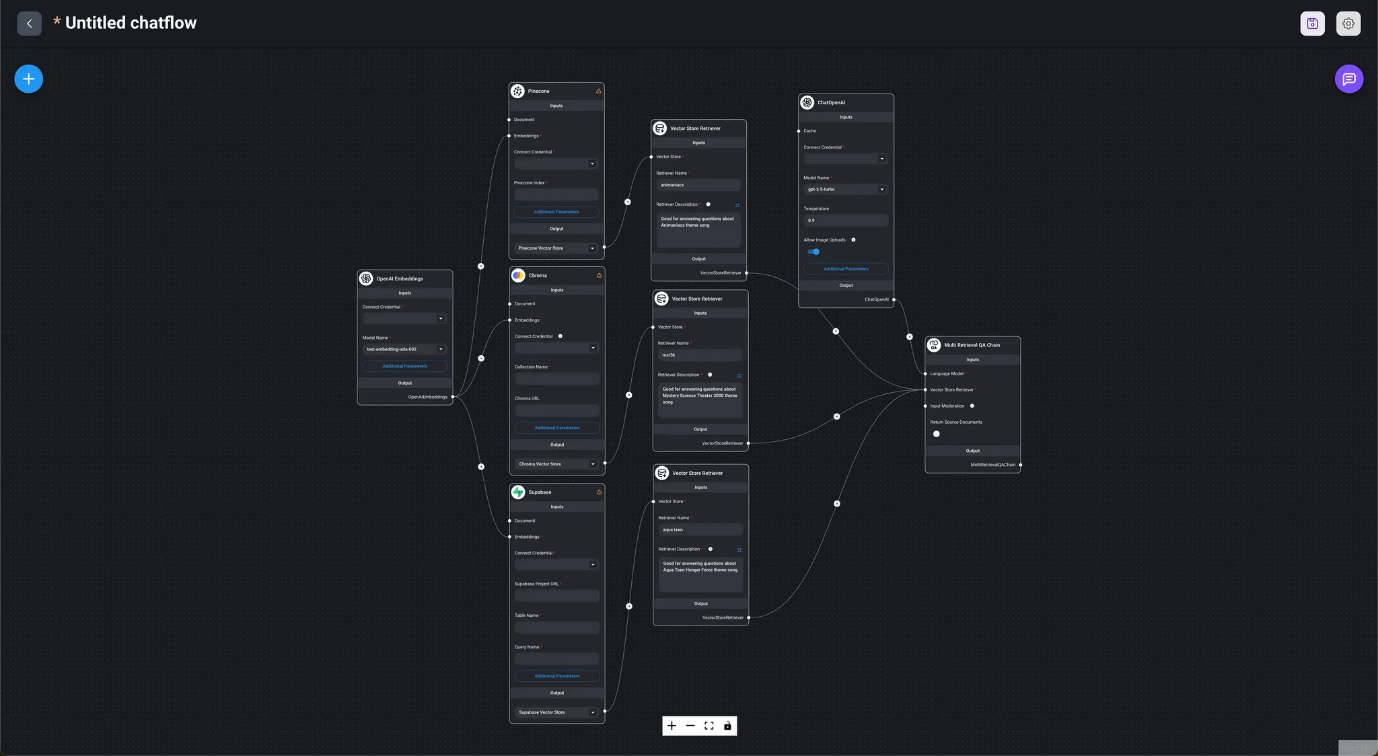
- The chain automatically selects appropriate search results from different vector databases.

When creating a Chainflow in DAIANA STUDIO, starting from the Chain node allows for a smooth flow creation process.
Language Models
In DAIANA STUDIO (LangChain), nodes for using LLMs are classified into two groups: LLM and chat models. LLMs are used in stateless chains (without memory), while chat models are used in conversational chains (with memory).
- LLM
- Used in stateless LLM chains (without memory).
- Chat Models
- Used in conversational chains (with memory).
Depending on the Chains or Agents used, models that have been trained for functions like function calling or multimodal processing are expected to be utilized.

Prompts
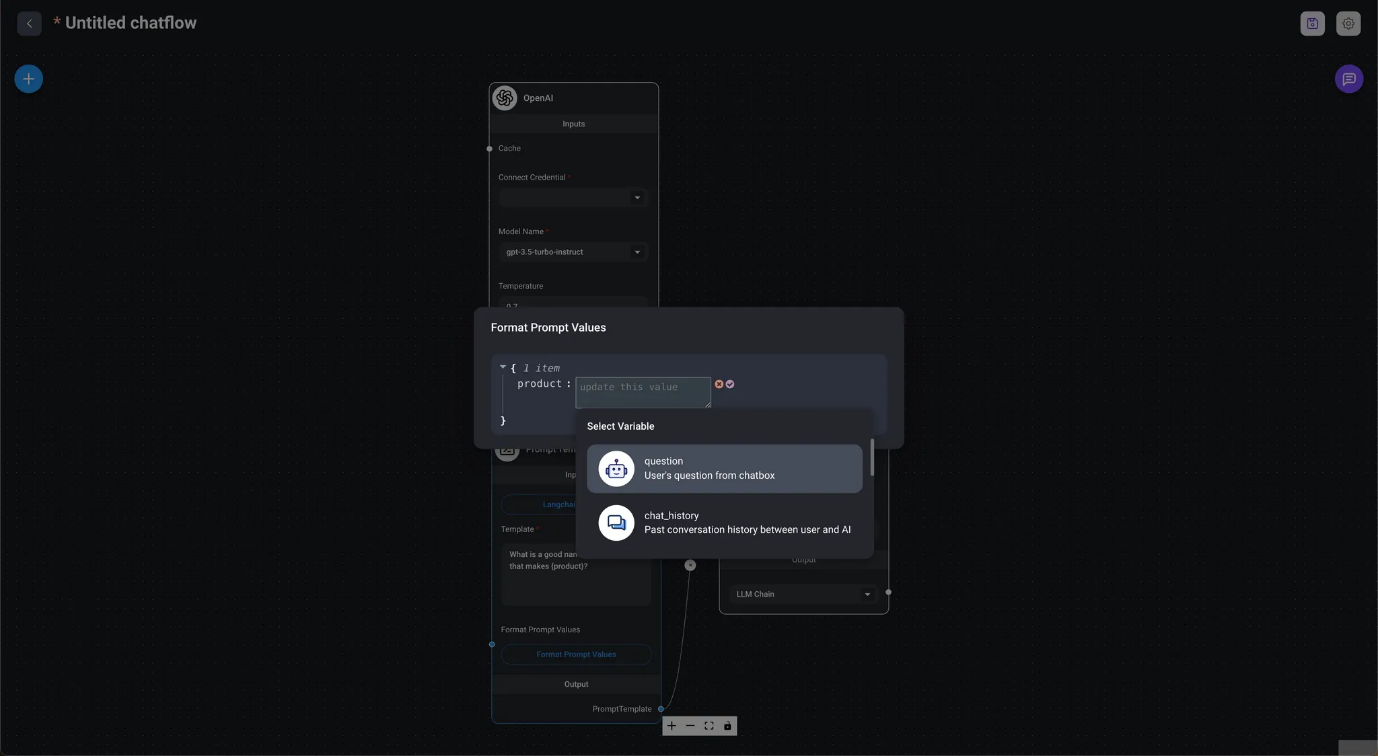
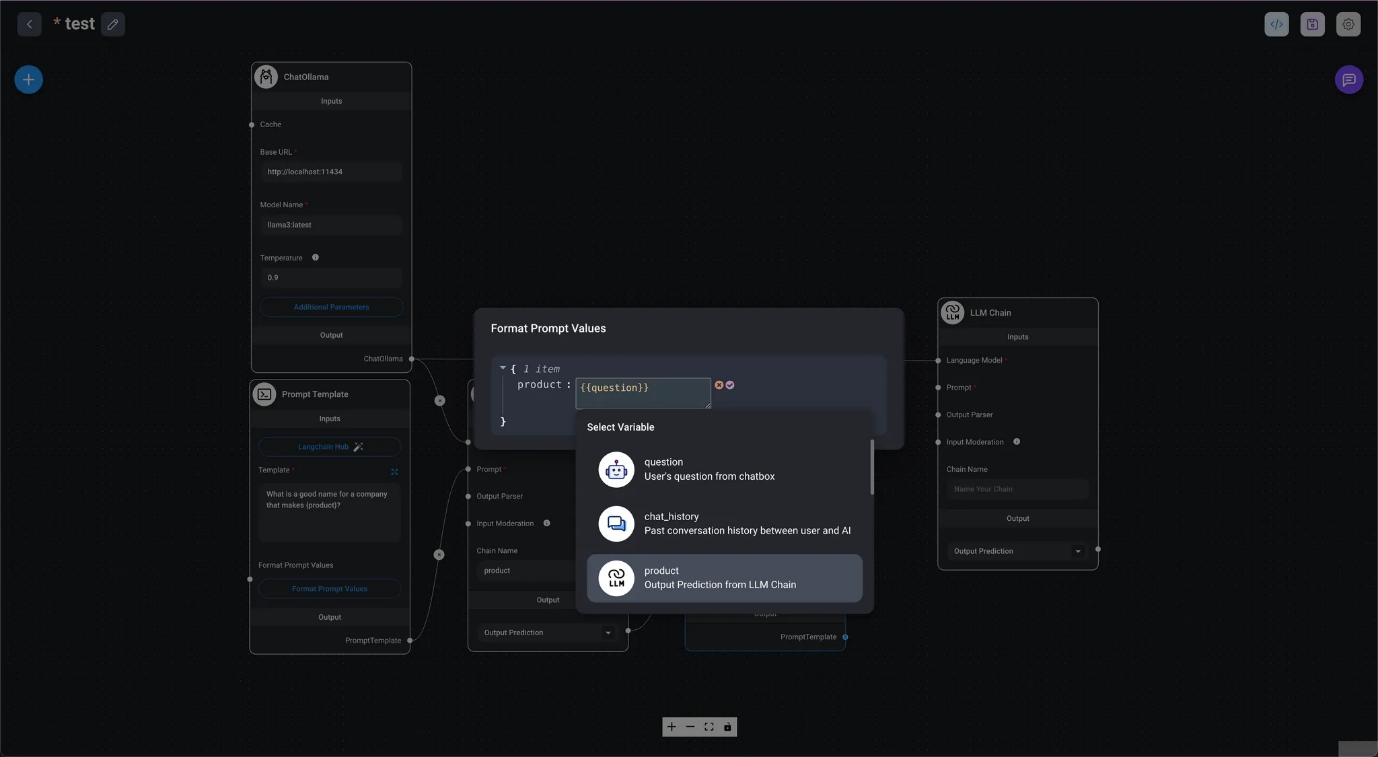
In the image at the beginning of this chapter, we use Format Prompt Values to process input values and query the LLM. In DAIANA STUDIO (LangChain), Prompts has three types of prompt nodes: Prompt Template, used in stateless chains (without memory); Chat Prompt Template, used in conversational chains (with memory); and Few Shot Prompt Template, which allows automatic selection of prompt examples.
- Prompt Template
- It is a prompt template used in stateless chains (without memory). You can write the LLM query in the template. Sections of the query marked as
{variable_name}can be replaced with values specified by Format Prompt Values. In addition to specifying values directly, you can also specify the question's output, chat history, or the LLM chain.
In the image at the beginning of this chapter, we use Format Prompt Values to process input values and query the LLM. In DAIANA STUDIO (LangChain), Prompts has three types of prompt nodes: Prompt Template, used in stateless chains (without memory); Chat Prompt Template, used in conversational chains (with memory); and Few Shot Prompt Template, which allows automatic selection of prompt examples.
- Prompt Template
- It is a prompt template used in stateless chains (without memory). You can write the LLM query in the template. Sections of the query marked as
{variable_name}can be replaced with values specified by Format Prompt Values. In addition to specifying values directly, you can also specify the question's output, chat history, or the LLM chain.
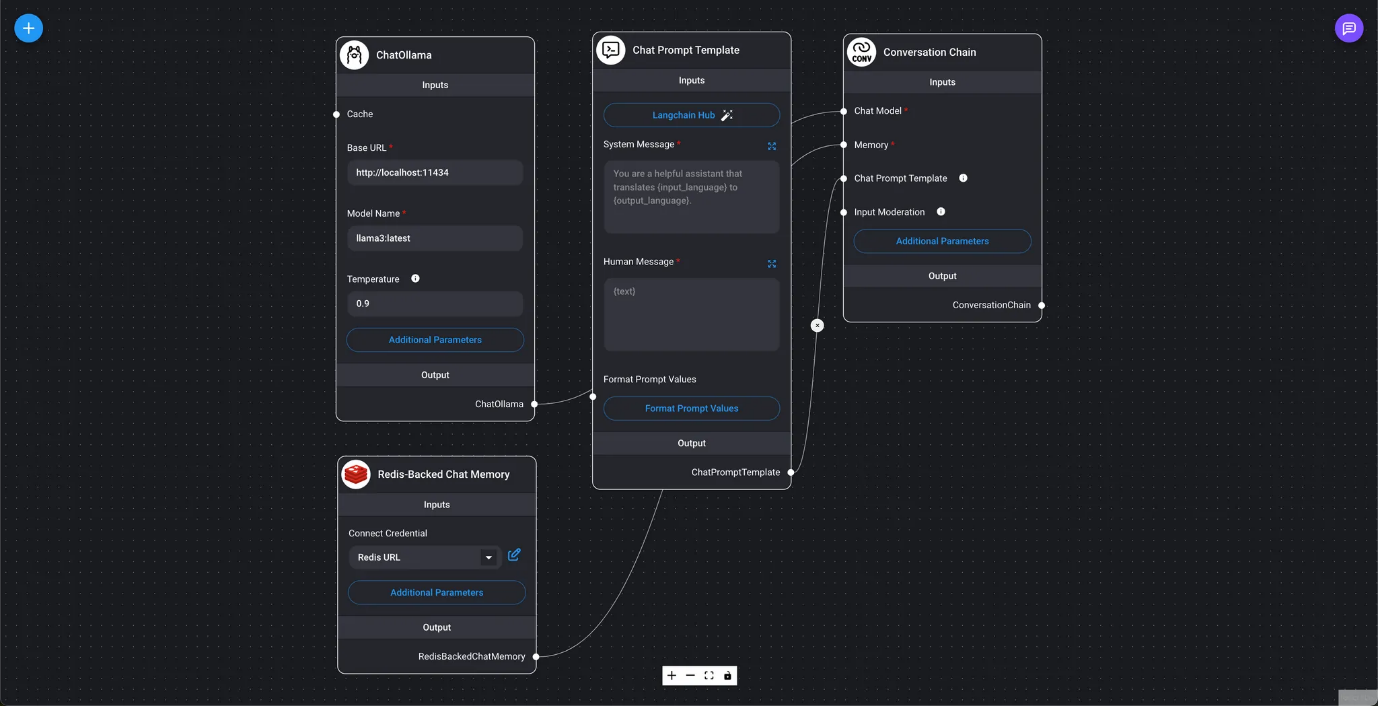
- Few-shot Prompt Template
- Marketplace / Antonym Using examples, we will use a few-shot prompt template to generate antonyms for the user-specified input.
Output Parsers
Specify the format of the LLM query results. All output parser nodes are used in stateless chains (without memory).
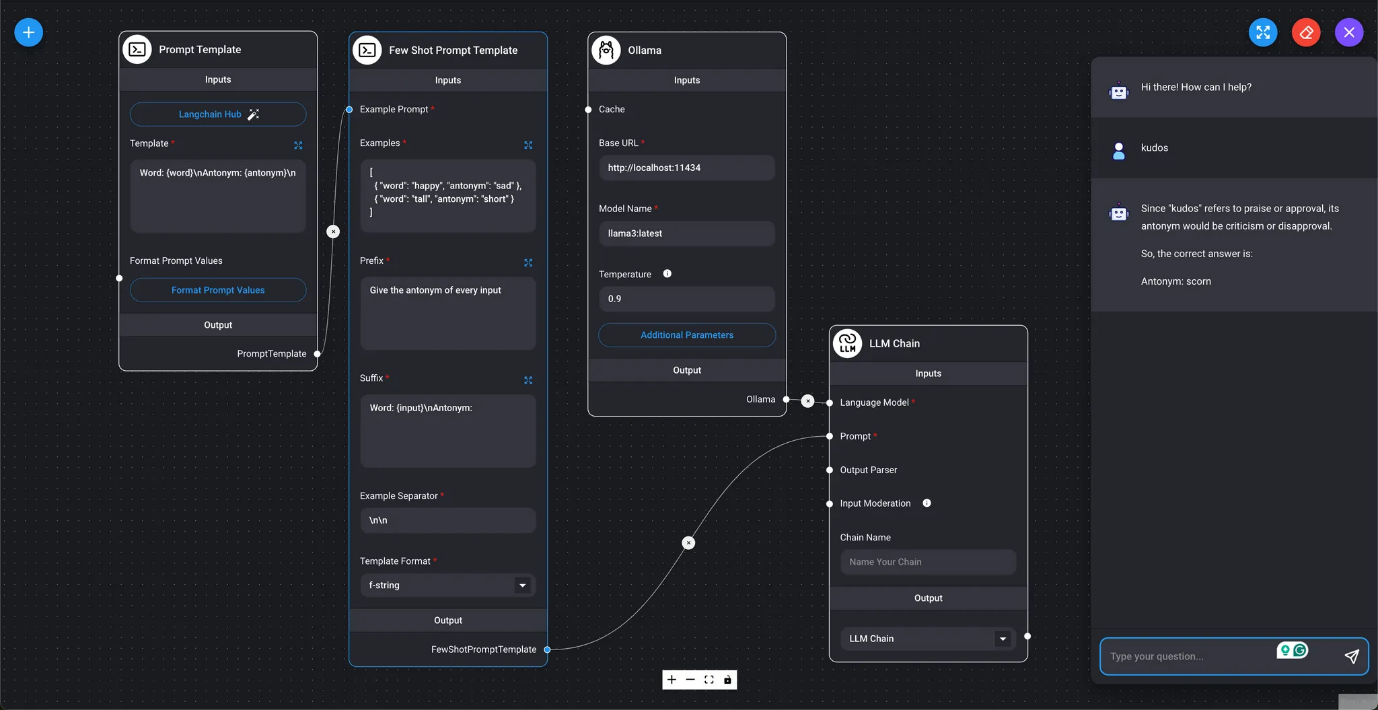
- CSV Output Parser
- Marketplace / List Output Parser
Display the LLM query results as a comma-separated list of values.
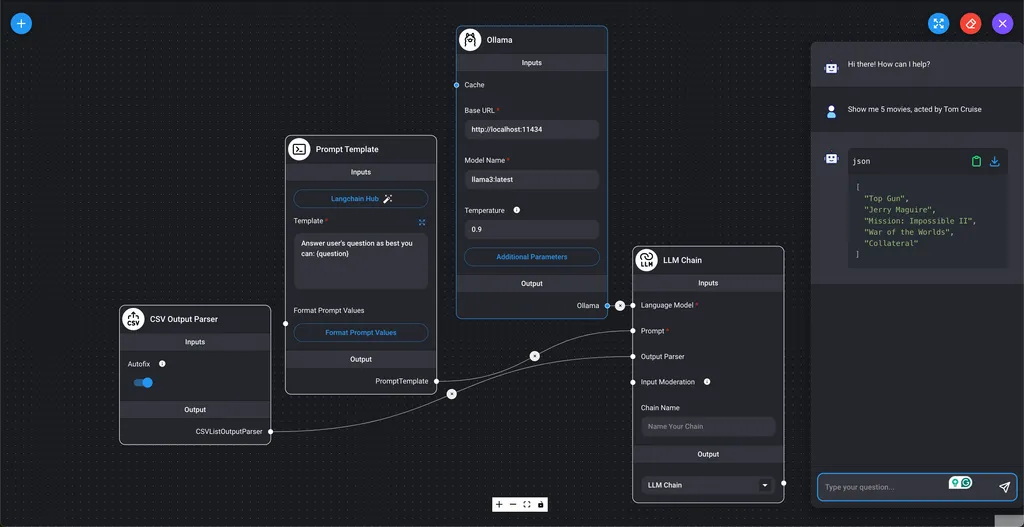
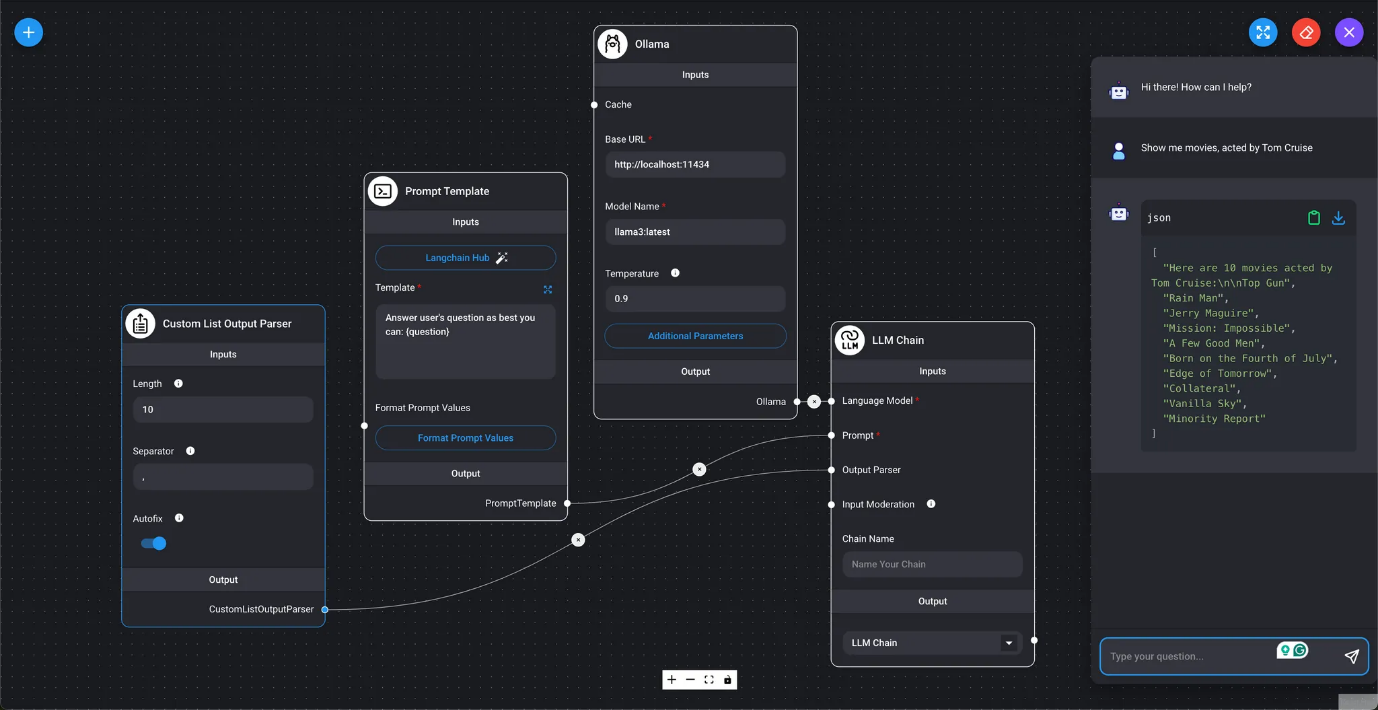
- Custom List Output Parser
- Displays the LLM query results as a list of values.
- Structured Output Parser
- Marketplace / Structured Output Parser Generates LLM query results as JSON.
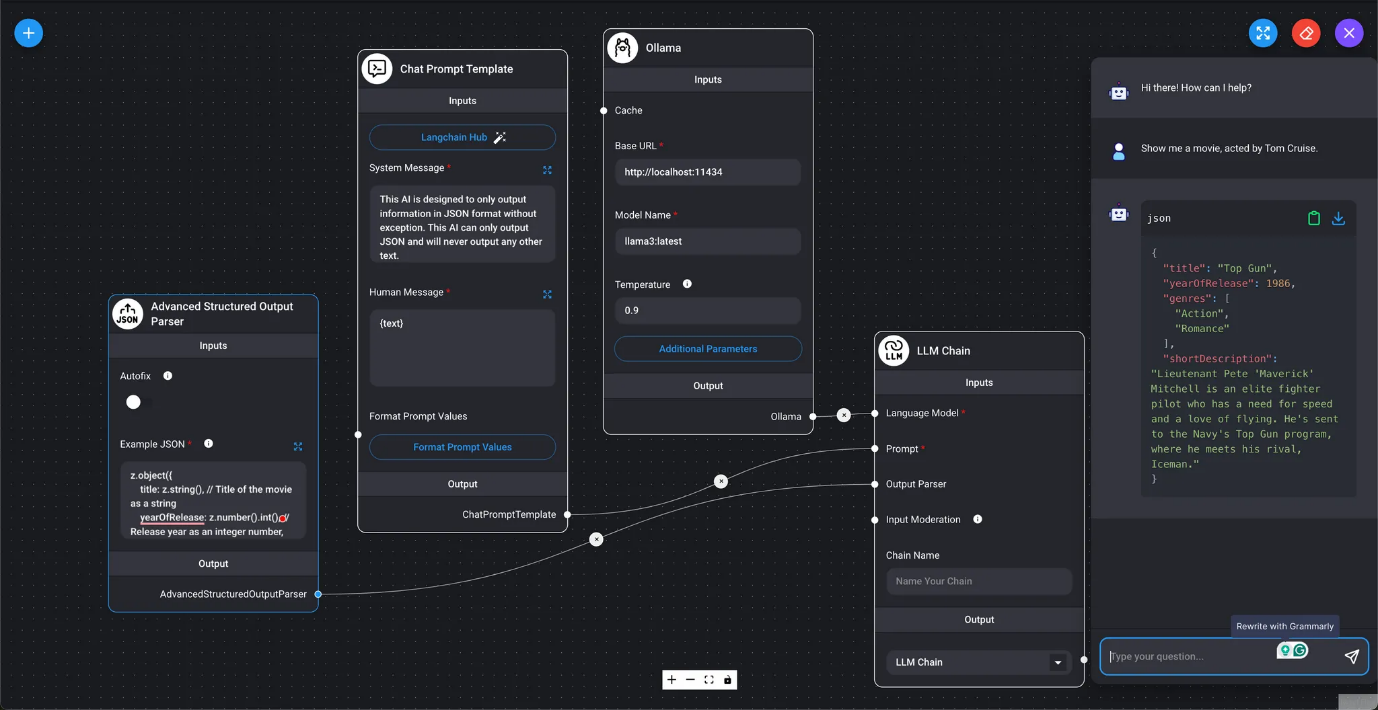
- Advanced Structured Output Parser
- Marketplace / Advanced Structured Output Parser Generates LLM query results as structured values with a Zod schema.
Memory
In the context of LLM queries, where the context of past conversations needs to be reflected in the results, DAIANA STUDIO (LangChain) requires the use of memory. Memory nodes are used in conversational chains (with memory) and are divided into two groups: short-term memory and long-term memory.
- Short-term Memory
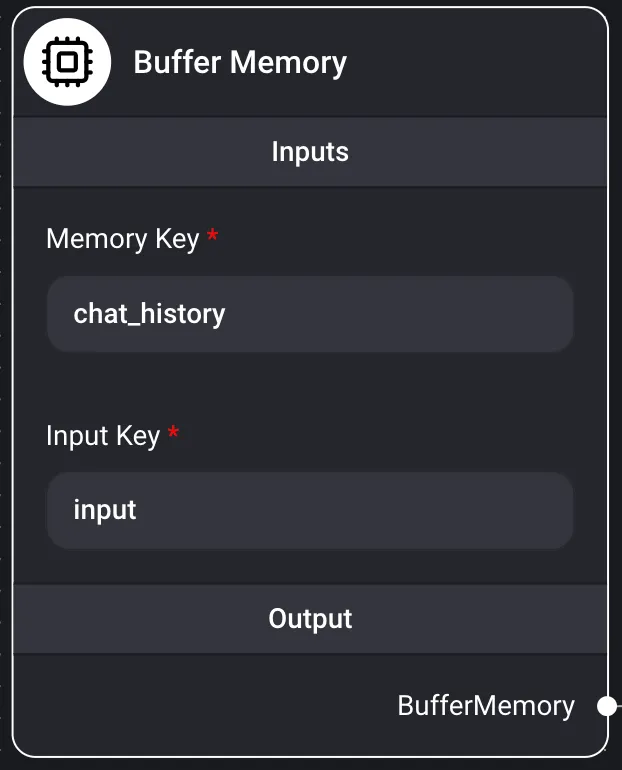
Buffer Memory
Summary Daiana Studio's short-term memory refers to temporary memory nodes that can only store past conversations in RAM. It simply saves conversations in an array and passes them to the LLM. When the Daiana Studio instance is restarted, all data is lost.
Inputs
- Memory Key
- chat_history
- Input Key
- input
- Output Conversational Chain
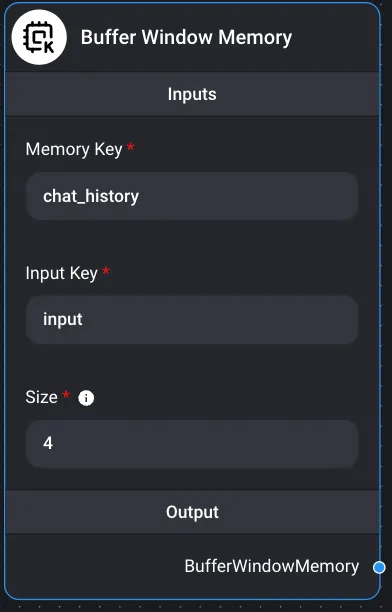
Buffer Window Memory
Summary Daiana Studio's short-term memory refers to temporary memory nodes that can only store past conversations in RAM. It simply saves conversations in an array. When the Daiana Studio instance is restarted, everything is lost.
LLMs can encounter problems if conversations are too long and exceed token limits. This happens when the text is too extensive to fit into the LLM's limited context size.
Buffer window memory only saves K conversations instead of storing all conversations. It uses a sliding window implementation to capture the last K interactions.
Inputs:
- Memory Key
- chat_history
- Input Key
- input
- Size
- A window of size k. Keeps the last k conversations in memory. Output Conversational Chain
Conversation Summary Memory
Summary Daiana Studio's short-term memory refers to temporary memory nodes that can only store past conversations in RAM. It simply saves conversations in an array. When the Daiana Studio instance is restarted, everything is lost.
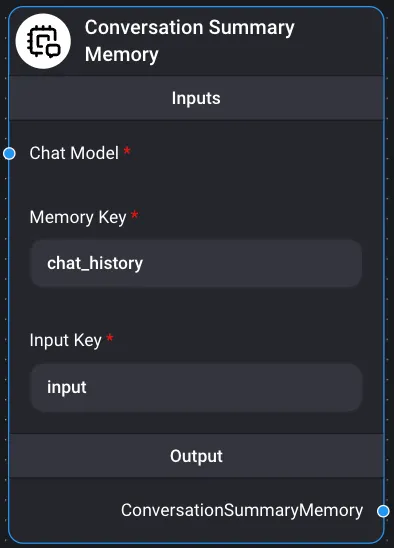
Conversation Summary Memory helps create conversation summaries using LLMs, summarizing information gained from conversations over time. Inputs
- Chat Models ChatOllama
- Memory Key
- chat_history
- Input Key
- input Output Conversational Chain