Training Console
Training Console
What is the Training Console?
The training console is an advanced tool designed for users to upload structured information.
This information is used by the model to generate accurate answers, detailed graphs, and logical SQL queries.
By using this console, the model is trained to better understand the questions asked and respond effectively, using the provided data and rules.
Available Training Types
In the training console, you can upload information in three main categories:
- DDL
- Documentation
- SQL
What it is:
- Represents the structure and definition of databases. Includes tables, columns, data types, relationships, and constraints.
- Allows the training console to understand how data is organized and what information it can extract.
DDL Example:
CREATE TABLE employees (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
ales DECIMAL(10, 2),
department_id INT,
hire_date DATE
);
How it's used
- Uses this information to validate queries and ensure that questions are answered with the available real data.
- Helps generate accurate SQL queries based on the database structure.
What it is:
- It is the set of rules, examples, and descriptions that are uploaded to guide its behavior in specific situations.
- Includes explanations on how to generate graphs, how to interpret questions, and what approach to take when responding.
Documentation Example: For questions related to total sales per employee:
- Use a bar chart to compare employees.
- The X-axis should show employee names.
- The Y-axis should show total sales.
- If a time period is specified, filter data by year or month.
How it's used
- Defines business rules and expected behavior for specific cases.
- It is useful for resolving ambiguities in questions and prioritizing certain approaches or chart types.
What it is:
- Represents specific SQL queries used to extract data directly from the database.
- Serves as a library of examples of how queries should be structured for different types of questions.
SQL Example:
SELECT name,SUM(sales) as Total_sale
FROM employees
WHERE hire_date>= '2023-01-01'
GROUP BY name
ORDER BY total_sales_DESC
How it's used
- Generates queries dynamically based on the user's questions and uses the trained SQL queries as templates.
- Ensures that queries are accurate and relevant to the use case.
How is Training Used?
- The training console uses the uploaded elements in a complementary way:
- DDL
- Documentation
- SQL
- It is the structural knowledge base. Without this information, it cannot understand how data is organized.
- Guides the logical and visual approach to responses (charts, tables, etc.).
- It is particularly useful for resolving ambiguities or visualization preferences.
- Provides practical and predefined examples to help generate fast and efficient queries.
Does Training Have Any Priority?
No priority based on upload order:
- No greater weight is assigned to the first training uploaded compared to the second or third. All uploaded elements are considered equally relevant.
Priority based on the query:
- If a query requires data interpretation, DDL has higher relevance.
- If a query is ambiguous or requires a specific chart, Documentation will have greater influence.
- If the question can be answered with a predefined query example, SQL will be prioritized.
Conflicts between training elements:
If there are contradictory rules (e.g., Documentation says to use a pie chart, but another document indicates to use bars), the console will try to resolve the ambiguity based on the query's keywords.
Recommendations for Uploading Training
Clear structure Ensure that each training type is well-defined and there is no redundant or contradictory information.
Use specific examples: Provide examples in Documentation and SQL for common cases you anticipate in your system.
Regular updates: Review and update training to reflect changes in data or new requirements.
Debugging After uploading new elements, perform tests with related questions to validate that the training console is responding correctly.
Conclusion
The training console is a tool that, when used correctly, can maximize the accuracy and relevance of generated responses and graphs.
By understanding how the different training types (DDL, Documentation, and SQL) are used and how the training console prioritizes information, you can ensure a more efficient system focused on user requirements.
How to upload training from Daiana?
From our assistant's settings, we must go to the training section.
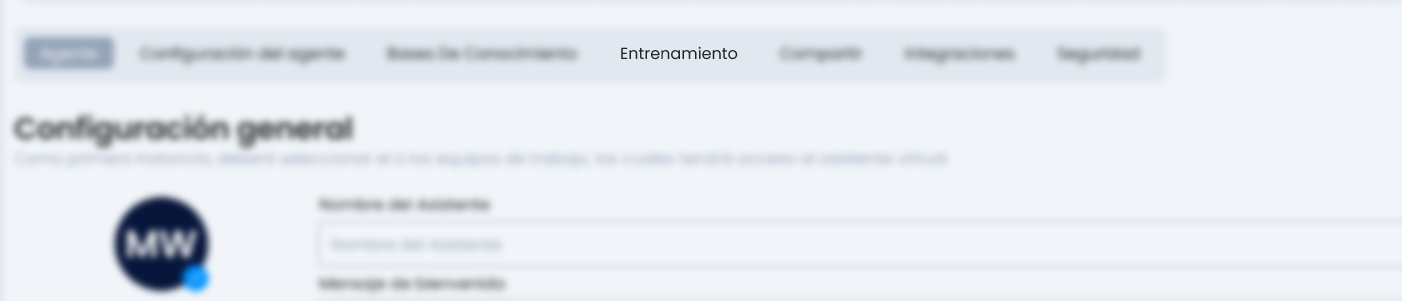
In this section, we must have all the credentials of our "Training Console" loaded to be able to go to the "Training" section. These credentials are obtained through the PI team.
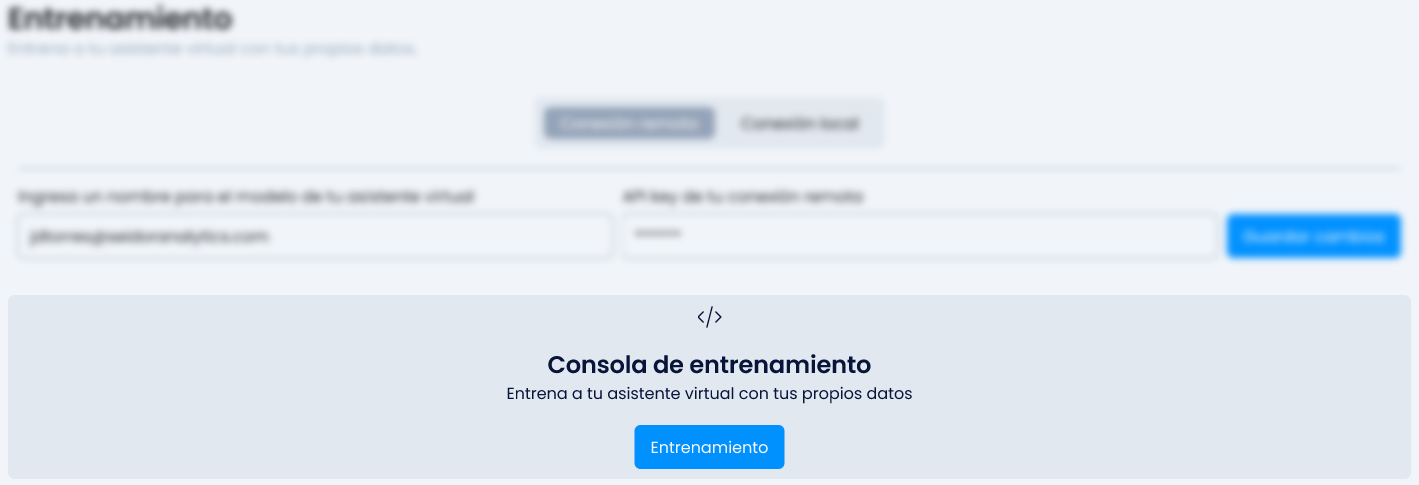
In our upper left corner, we will see the Seidor logo and click on "Training".

To add training, click the blue button.
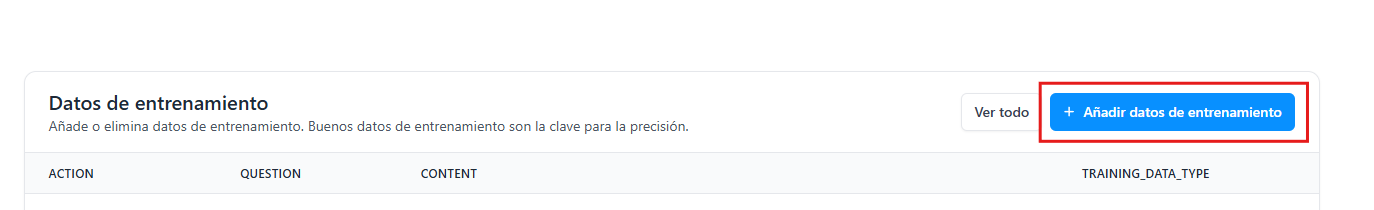
Taking into account our needs to train our assistant and considering the type of training we need to add, we select "training type".
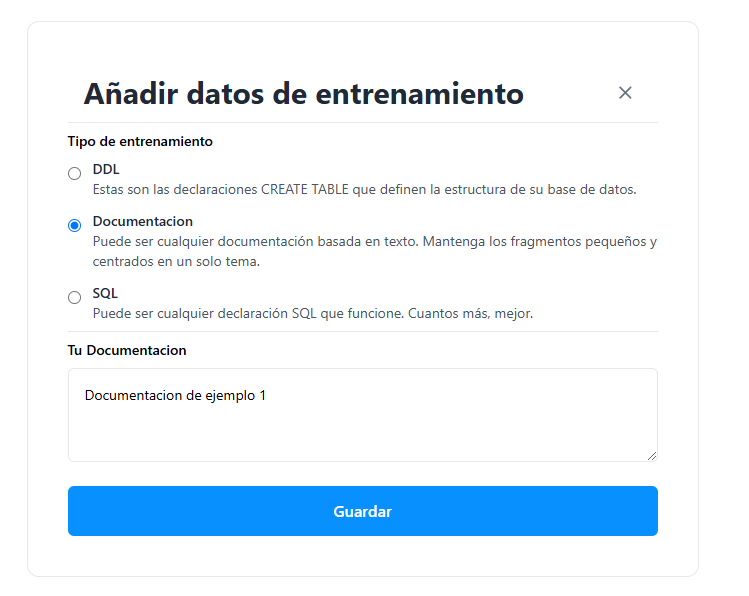
Once we add the desired training in the input field, we click save, and our assistant will now take into account the added training.
How to replace an added training?
Currently, we cannot edit the added training, so we must find the previously added training and delete it using the Delete button, then re-upload the updated training.
Recommendations
Recommendations to optimize the responses of a database assistant.
Upload the database structure as DDL:
- Make sure to upload the database structure as DDL. This helps the assistant understand how information is organized, including tables, columns, relationships, and data types.
- This way, the training console can accurately identify the necessary values to answer queries, avoiding errors related to non-existent or misinterpreted data.

Document frequently asked questions as "Documentation" type:
- For common questions, upload clear rules in the Documentation section. Define not only the expected response type but also the specific direction or column from which the value should be obtained.
- For example, if a frequent query is "What are the total sales per employee?", you can include in the documentation the rule indicating that sales should be calculated from the "sales" column grouped by "employee_name."
Problems due to Lack of Training
These are common causes of problems due to lack of training.
Insufficient or poorly structured data in the database (DDL)
Cause
- If the uploaded database structure (DDL) is incomplete or contains errors, the training console will not be able to correctly interpret queries or generate logical responses.
Manifestations
- Does not find columns or tables requested in questions.
- Generated SQL queries are incorrect because they do not take into account relationships or data types.
- Empty graphs or graphs based on non-existent data.
Example
- If an employee table does not include a field for "total sales," the training console will not be able to answer questions about "How much did each employee sell?"
Vague or ambiguous rules in Documentation training
Cause
- Instructions in Documentation are not clearly defined or do not cover enough use cases, leading to inconsistent or meaningless responses.
Manifestations
- The training console chooses an incorrect chart type (e.g., generates a bar chart instead of a requested pie chart).
- Ambiguous or incomplete responses because there are not enough guidelines to interpret complex questions.
- Graphs with disordered labels and values.
Example
- If it is not specified that pie charts should show proportions, the training console might use another chart type that does not accurately reflect the data.
Incomplete or poorly designed SQL queries in training
Cause
- The SQL queries loaded in the training are not representative or are poorly designed, affecting the ability to generate data-driven responses.
Manifestations
- Incorrect or irrelevant responses to user questions.
- SQL queries are generated that return empty or incorrect results.
- Graphs that do not correspond to the expected data.
Example
- If the SQL query for sales does not filter by dates correctly, the responses will include irrelevant or outdated data.
Lack of coverage for frequent use cases
Cause
- The training does not include examples of relevant questions and answers for the most common use cases of the application.
Manifestations
- Does not respond or returns generic messages like "I don't know how to answer this question."
- Responses that don't make sense because they are not based on clear rules or examples.
- The model does not generate adequate graphs for complex or specific questions.
Example
- If the training console is not trained to answer questions like "What are the total sales by region in 2023?", the training console might fail to interpret this query.
Conclusion
To avoid these problems, it is essential to:
- Complete the DDL training with a detailed and correct database structure.
- Define clear rules in Documentation that address specific cases and graphical approaches.
- Design representative SQL queries and test them with real data.
- Expand training to include examples of frequently asked questions and key use cases.